
Diverticulosis and diverticulitis
What is diverticulosis?
What is diverticulitis?
Symptoms of diverticulosis
Symptoms of diverticulitis
Causes of diverticulosis and diverticulitis
Prevention / remedies / cures / treatment for diverticulosis
References
What is diverticulosis?
Diverticulosis is when you have one or more sacs or pouches in your gut.
A gut diverticulum is a hollow pouch or sac, usually about the size of a small pea, which balloons outwards through the wall of the gut. It can occur anywhere between the oesophagus and the colon, but 80% of them are found in the sigmoid colon, which is just above the rectum. This may be because that is where the colon is the narrowest and the inner pressure the highest.
A true diverticulum forms through all three layers of the gut: the mucosa lining, the muscle, and the outer serosa. False diverticula do not form through the muscle, so they are thin-walled. Colonic diverticula are typically false.
Healthy babies are born without colonic diverticula. They are not common in people less than 40 years of age, but by the age of 60 more than half of all adults in Western countries have at least one and usually a few dozen. (1, 2) Diverticulosis is almost unheard of in those populations living on their traditional diets in non-Westernised parts of the world.
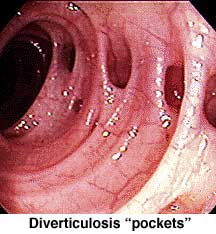
What is diverticulitis?
Diverticulitis is an inflamed diverticulum.
Sometimes these pockets hold faecal matter as the body's waste moves through the colon. In rare cases, diverticula may bleed, perforate, block, or get infected or inflamed.
An abdominal abscess can also form. This is a severe condition which may require draining of pus or a colostomy.
Peritonitis is when faeces leaks into the abdominal cavity (peritoneum) through a tear or hole (fistula). The bacteria in the faeces cause a severe infection, which can be life-threatening and requires emergency surgery.
Symptoms of diverticulosis
Most people who have colonic diverticula are unaware that they have them, and usually colonic diverticula are of no significance. They are often accidentally discovered during the course of a barium enema x-ray, CT scan of the abdomen, flexible sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy, or surgery.
The diverticula themselves do not usually cause any symptoms. Diverticula often coexist with other painful conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), however they do not necessarily cause these conditions.
- Pain in the lower left abdomen (relieved after passing stool or gas).
- Abdominal bloating or cramps.
- Constipation or diarrhoea.
- Painless rectal bleeding, with bright red blood. Other ailments such as haemorrhoids can also cause rectal bleeding.
Symptoms of diverticulitis
- Severe abdominal pain (usually in the left lower of the abdomen). The pain can start suddenly, or may start mild and worsen over time.
Warning - several other ailments can also cause severe abdominal pain, such as pelvic inflammatory disease, appendicitis, irritable bowel syndrome, ischemic colitis, colon and various cancers. A doctor is required for diagnosis. - The abdomen is tender to touch.
- Fever (caused by the inflammation or infection).
- Constipation or diarrhoea, change of daily bowel habits.
- Blood in stool (bright red, rather than dark in colour).
- Nausea or vomiting.
Causes of diverticulosis and diverticulitis
It seems that relatively high pressures generated within the colon by muscular contractions force the inner mucosa to penetrate through the path of small blood vessels within the colon wall and to bulge beyond the serosa.
Why is the gut wall of some people weak enough for this to happen?
- The weakening of the colon wall is primarily caused by inflammation and the reaction of the gut to many of the toxins in a modern high-sugar, processed food diet.
The number one cause: a diet high in sugar, flour and oil from grains, and processed foods. (5) - Diverticula are less common in lifelong vegetarians.
- Aging. The strength of the colon wall usually declines with age. (4)
- Obesity.
- Hereditary or connective tissue disorders (such as Marfan syndrome and Ehlers Danlos Syndrome) that may cause weakness in the colon wall.
- Constipation is probably not a cause. Hard stool can exert more pressure on the colon wall. It may also move through the colon more slowly, causing a backup of stool behind it, which causes additional pressure. It is possible that sustained internal pressure from hard faecal matter in the diverticula can impair blood circulation and weaken the wall of the diverticulum, which may cause the pouch to burst. However, a study (3) in 2012 found that constipation is not associated with diverticulosis. On the contrary, it occurs more often in those who have more than 15 bowel movements per week. Again, this suggests that diverticulosis is a disease caused by a toxic, inflamed or upset gut. The study also showed that a high-fibre diet and increased frequency of bowel movements are associated with greater, rather than lower, prevalence of diverticulosis. A high fibre diet, and bran or psyllium supplements probably worsen diverticulosis.
There are several other factors which compromise the muscle tone of the colonic wall and weaken its lining:
Prevention / remedies / cures / treatment for diverticulosis
Those who have colonic diverticula and no symptoms can relax. Nothing is likely to happen because of them.
- Diet. Try to keep to a diet of traditional, unprocessed foods that are low in sugar and refined components. These are the foods that will impose the least inflammation on your colon.
- Chew your food well. It is possible that partially chewed, large pieces of nuts or seeds may lodge in the diverticula and provoke diverticulitis. In any case, I always advise people to chew their food well for optimum digestion.
- Use a natural squatting position for defecation. Humans evolved to use the squatting position, and it is only in the rich Western world that upright toilets are used.
- See details of remedies recommended by Grow Youthful visitors, and their experience with them.
References
1. Jones OJ.
Diverticular disease.
BMJ 1992;304:1435-7.
2. Comparato G, Pilotto A, Franze A, Franceschi M, Di Mario F.
Diverticular disease in the elderly.
2007, Digestive diseases (Basel, Switzerland) 25 (2): 151-9. doi:10.1159/000099480. PMID 17468551.
3. Anne F. Peery, Patrick R. Barrett, Doyun Park, Albert J. Rogers, Joseph A. Galanko, Christopher F. Martin, Robert S. Sandler.
A High-Fiber Diet Does Not Protect Against Asymptomatic Diverticulosis.
Gastroenterology, February, 2012.
4. Iwasaki, cited by Yamade, M.A.B.A.
Strength of biological materials.
Baltimore, Williams and Watkins, 1970.
5. Wess L, Eastwood MA, Wess TJ, Busuttil A, Miller, A.
Cross linkage of collagen is increased in colonic diverticulosis.
1995, Gut 37 (1): 91-94. doi:10.1136/gut.37.1.91. PMC 1382775. PMID 7672689.
